The sun and aging. Do they have anything in common?

Aging is generally caused by multiple factors including genetics, lifestyle and environmental factors. However, according to research, excessive exposure to sunlight is responsible for up to 80% of aging1!
Photoaging is damage to the skin that is excessively exposed to the sun's UV rays over a long period of time. It can cause wrinkles, pigmentation, uneven skin tone or sagging1. A cream with a high SPF and PA factor is therefore an essential part of the cosmetic routine to prevent the harmful effects of UV radiation on the skin.
Solar spectrum
Before we talk about what sunscreen actually is, it would be good to explain why we need it at all. The sun provides us heat through infrared radiation (>780nm), lighting due to which we can actually see our surroundings through visible radiation (400-780nm), and also ultraviolet radiation, which we can neither see nor feel (<400nm).
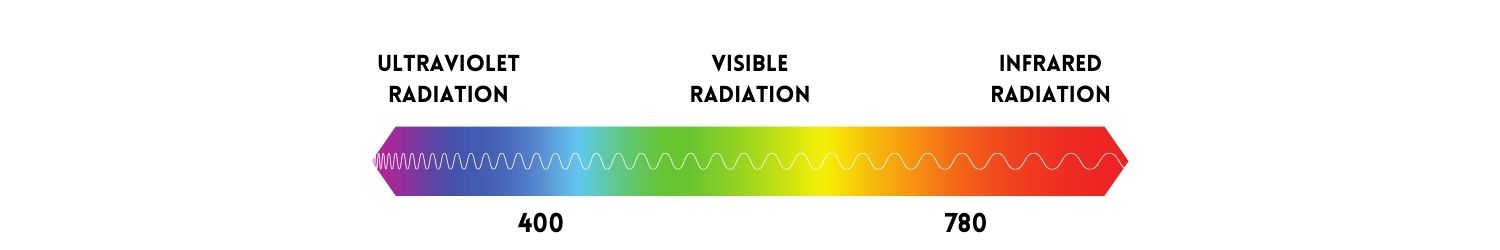
Ultraviolet radiation and its effect on the skin
Ultraviolet radiation is proven to be a human carcinogen2, which means it increases the risk of skin cancer. Of course, the sun also provides benefits, no doubt about that. One of them is the production of vitamin D with the help of UVB radiation from precursors found in the skin. Therefore, it is ideal to find a balance between the benefits and allow the skin to create vitamin D, while protecting it from harmful UV radiation.
When we talk about UV radiation, we mean anything up to 400nm. In the range from 0 - 280 nm there is UVC radiation, which, however, does not even penetrate our ozone layer. Another is UVB radiation, which is in the range of 280-320nm. It makes up approximately 5% of the total UV radiation. And then there is UVA radiation, which ranges from 320-400nm.
UVB radiation hits the skin superficially and causes it to tan/burn. Burning the skin results in an increased risk of skin cancer. While UVA radiation penetrates deep into the skin and contributes to premature aging of the skin - i.e. to the breakdown of collagen, the formation of wrinkles, and also to skin cancer. What is important to emphasize, UVA radiation also penetrates through glass! So if you sit all day in the office by the window or drive in a car, don't forget to apply a cream with SPF and PA factor :)
What is SPF?
SPF - Sun Protection Factor ((translated as sun protection factor) was originally created to determine protection against UVB radiation in sunscreen - i.e. as a degree of protection against burning. That is, it does not reflect protection against UVA radiation (aka premature aging). Basically, SPF refers to the amount of time it takes for the skin to burn when using sunscreen. For example, if it takes my skin 10 minutes to burn in the sun without sunscreen, it will take 15 x 10 (i.e. 150 minutes) to reach a similar level of skin burn if I use SPF15. Maybe it will seem great that in that case SPF15 is completely enough for me. A mistake! Because SPF15 blocks only 94% of UVB radiation, whereas SPF30 blocks up to 97% of UVB radiation and SPF50 blocks up to 98% of UVB radiation. And maybe it seems that it is quite a small difference, in fact, a higher factor protects us much more. The ideal sunscreen should be in the range of SPF 30-50. According to dermatologists, novelties on the market declaring SPF100 have no greater added value than creams with a lower SPF, because rather they can be harmful in the sense that people think they will protect them twice as long, and thus give a false sense of security3. It happens that people with such a high factor tend to stay in the sun longer without reapplying the cream.
PA system
UVA protection in sunscreens has only become a topic in the last few years. It can be seen included in the sunscreen cream as - protection against a broad spectrum of UV rays (broad-spectrum protection of UV rays). Currently, the PA system is the only one that is used to independently measure protection against UVA radiation. It is typical for Asian cosmetics, especially Korean cosmetics. It is marked from PA+, PA++, PA+++ to PA++++. The higher the value, the greater the protection against UVA radiation.
Chemical and. physical filters
There are two types of SPF filters in sunscreens:
- chemical / organic - absorb UVB radiation and convert it into heat, which is carried away from the body by thermoregulation. They are easy to apply
- physical / mineral / inorganic - reflect UVB radiation back to the outside environment. Their biggest disadvantage is that they are difficult to spread and leave white traces (zinc oxide, titanium dioxide)
What type of sunscreen to use?
It is ideal to decide according to your skin type. If you have dry skin, look for sunscreen in the form of a moisturizer. In the case of oily skin, or acne-prone skin, look for sunscreens that are non-comedonic and have a gel form, or cream-gel. If you have sensitive skin, look for the label "hypoallergenic".
It is important to mention that photoaging occurs throughout the year, although it is more pronounced during the summer months. Therefore, it is important to protect yourself from the sun all year round.
Sources:
1 Flament, 2013. Effect of the sun on the visible clinical signs of aging in Caucasian skin.
2 American Cancer Society, 2019. Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation.
3 EWG, 2015.